Shockwave Therapy
section-af655b2
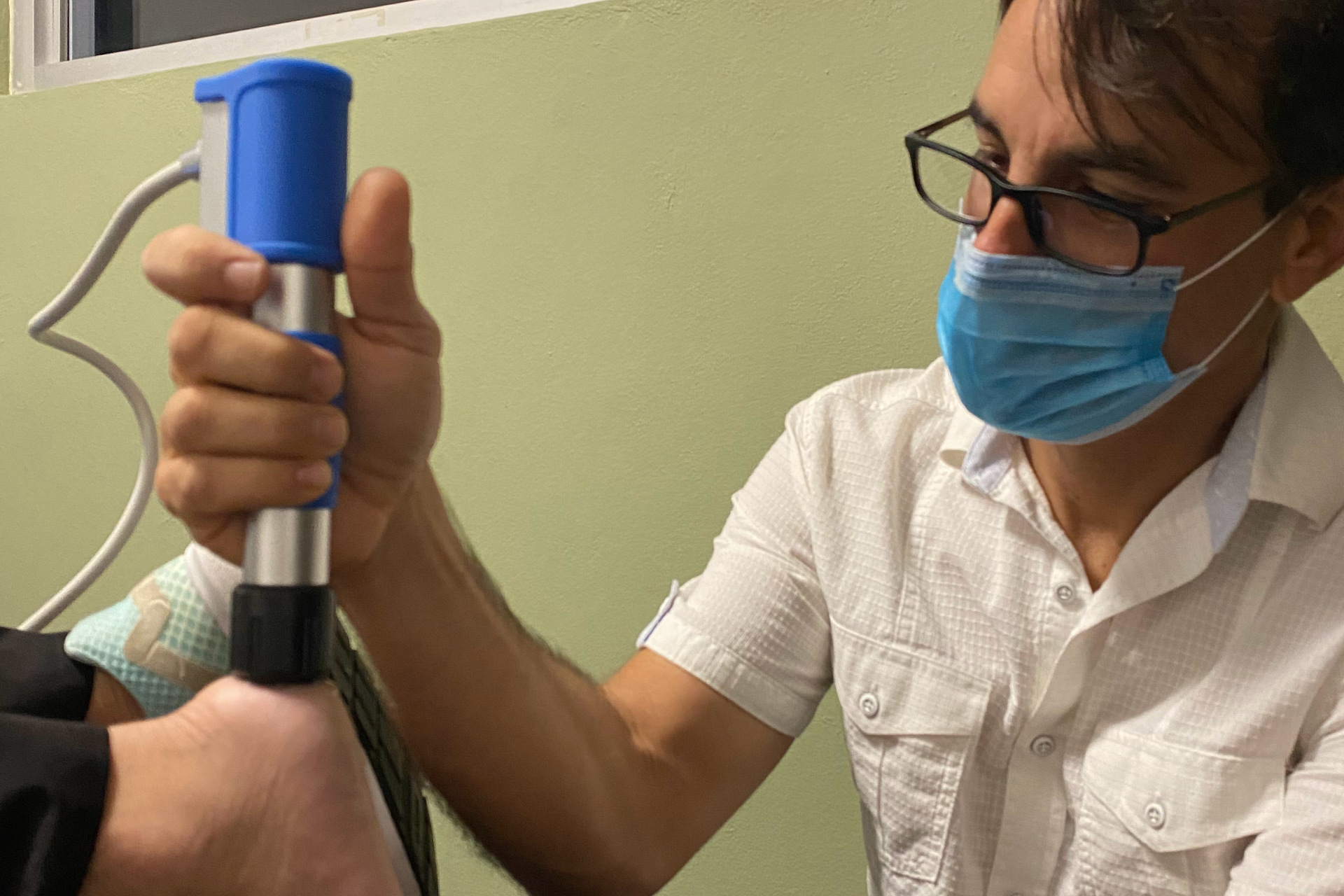
Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)
Shockwave therapy is a modality that is becoming more common in the field of physical therapy, as well as other health care fields. Shockwave therapy, or extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT), is used in the treatment of many musculoskeletal conditions, primarily those involving connective tissues such as ligaments and tendons. One of the most common conditions treated with shockwave therapy is plantar fasciitis.
Orthopedic conditions commonly treated with shockwave therapy include:
- Plantar fasciitis
- Jumper’s knee (patellar tendinitis)
- Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)
- Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis)
- Achilles tendinitis
- Bursitis
- Rotator cuff pain
- Chronic pain
- Stress fractures (bone healing)
- Morton’s Neuroma
How does shockwave therapy work?
Shockwave therapy works by emitting high energy pulses. These pulses of acoustic energy are focused on the target tissues by the handpiece / applicator of the shockwave therapy machine and are believed to cause localized microtrauma that stimulates the bodies natural healing processes.The shock waves are believed to stimulate angiogenesis / neovascularization (new blood vessels) and neurogenesis (new nerve cells). The microtrauma increases local circulation and enhances breakdown of calcifications (calcium build-up).